Individual Rows can be Replaced
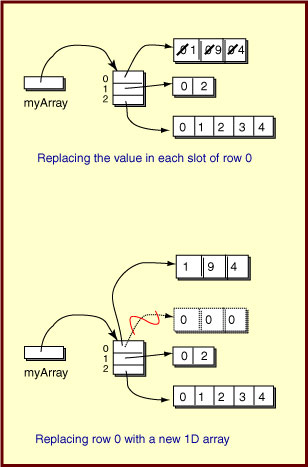
The following answer will not work:
myArray[0] = {1, 9, 4} ;
An initializer list can only be used to initialize an array, not to assign values to it during a run of a program.
If your answer was:
int[] x = {1, 9, 4} ; // declare and init x
myArray[0] = x ; // assign to myArray
This will work, but does not quite do what the question asked. The suggested answer puts the values into the required slots of the existing 1D array object of row 0.
The not-quite-right answer replaces the old
row 0 by constructing a new 1D array object
holding the desired values in its slots,
then assigning that object to row 0 of myArray.
The previous row 0 is now garbage.
Both answers result in myArray containing what you want.
In most programs it will not matter which method you used.
