Adding Elements to a Vector
To add an element to the end of a Vector use:
addElement( Object ) ; // add a reference to an Object to the end of the Vector,
// increasing its size by one. The capacity of the Vector
// will increase by increment if needed.
Here is an example program.
To use the Vector you must import the java.util
package:
|
import java.util.* ;
class VectorEg
{
public static void main ( String[] args)
{
Vector names = new Vector( 20, 5 );
System.out.println("capacity: "
+ names.capacity() );
System.out.println("size: "
+ names.size() );
names.addElement("Amy");
names.addElement("Bob");
names.addElement("Cindy");
System.out.println("capacity: "
+ names.capacity() );
System.out.println("size: "
+ names.size() );
}
}
|
The initial capacity of the Vector is set to 20 with an
increment of 5.
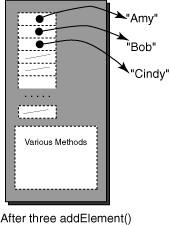
References to three String objects are added.
(The String objects are constructed
by enclosing characters in quote marks.)
As the diagram shows,
the added objects are not part of the Vector.
The Vector contains an array of references
to the objects added to it.
