Starting the Program
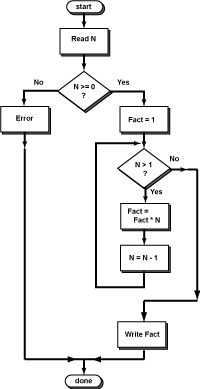
Here is a start to the program.
import java.util.Scanner;
// User enters integer N.
// The program calculates N factorial.
//
class factorial
{
public static void main (String[] args )
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in );
long N, fact = 1;
System.out.print( "Enter N: " );
N = scan.nextLong();
if ( )
{
while ( )
{
;
;
}
System.out.println( "factorial is " + fact );
}
else
{
System.out.println("N must be zero or greater");
}
}
}
Notice how the program matches the flowchart,
especially how the while statement is
nested in the true branch of the if statement.
The indenting (and the braces {} show this structure).