Two Strings that are == are always equal()
The == determines if two
names both refer to the same object.
It is common in the real world (and in programs) for an object to
have several names, for example "Mark Twain" and "Samuel Clemens"
are two names for the same author.
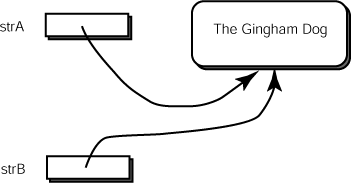
Consider two strings:
String strA = new String ("The Gingham Dog");
String strB = strA;
- Since there is only one object,
strA == strB - Since both reference variables point to an object with the same data,
strA.equals( strB )
If ==
is true, then so does equals().