Theorem: For all
Theorem: For all
![]() ,
,
Proof:
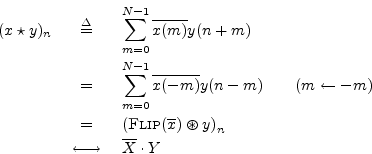
The last step follows from the convolution theorem and the result
![]() from §7.4.2. Also, the
summation range in the second line is equivalent to the range
from §7.4.2. Also, the
summation range in the second line is equivalent to the range
![]() because all indexing is modulo
because all indexing is modulo ![]() .
.