communicator
A communicator is an opaque object with a number of attributes,
together with simple rules that govern its creation, use and
destruction. The communicator specifies a communication domain
which can be used for point-to-point communications.
communication domain
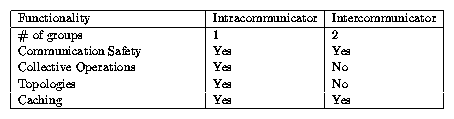
An intracommunicator is used for communicating
within a single group of processes; we call such communication intra-group communication. An intracommunicator has two fixed
attributes.
intracommunicator
intra-group communication domain
These are the process group and the topology describing the logical layout
of the processes in the group. Process topologies are the
subject of chapter ![]() . Intracommunicators are also
used for collective operations within a group of processes.
. Intracommunicators are also
used for collective operations within a group of processes.
An intercommunicator is used for point-to-point
intercommunicator
communication between two
disjoint groups of processes. We call such communication inter-group
communication.
inter-group communication domain
The fixed attributes of an
intercommunicator are the two groups. No topology is associated
with an intercommunicator.
In addition to fixed attributes a
communicator may also have user-defined attributes which are associated
with the communicator using MPI's caching mechanism, as described in
Section ![]() . The table below summarizes the differences
cachingcommunicator, caching
between intracommunicators and intercommunicators.
communicator, intra vs inter
. The table below summarizes the differences
cachingcommunicator, caching
between intracommunicators and intercommunicators.
communicator, intra vs inter
Intracommunicator operations are described in
Section ![]() , and intercommunicator operations are
discussed in Section
, and intercommunicator operations are
discussed in Section ![]() .
.