Opposite Direction
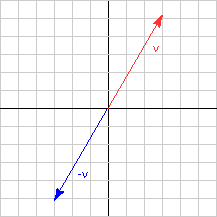
You can see this mechanically:
| v | = |(a, b, c)T| =( a2 + b2 + c2) |-v | = |(-a, -b, -c)T| =
( -a2 + -b2 + -c2 ) =
( a2 + b2 + c2 )
The diagram shows this graphically (in two dimensions).
You would like to say that the two vectors are the same length, but point in opposite directions. In fact, you can say that. The next chapter will give you the authority to do so.
