The sendmail program implements the SMTP (and
ESMTP) HELP command by looking up help messages in a text file.
Beginning with V8.7 sendmail, help messages for
the -bt rule-testing mode are also looked up in
that file. The location and name of that text file are specified by
using the HelpFile option. If the name is the
C-language value NULL, or if sendmail cannot
open that file for reading, sendmail issues the
following message and continues:
502 5.0.0 HELP not implemented
The help file is composed of lines of text, separated by tab
characters into two fields per line. The leftmost field is an item
for which help is offered. The rightmost field (the rest of the line)
is the help text to be printed. A few lines in a typical help file
might look like this:
help HELP [ <topic> ]
help The HELP command gives help info.
helo HELO <hostname>
helo Introduce yourself.
ehlo EHLO <hostname>
ehlo Introduce yourself, and request extended SMTP mode.
ehlo Possible replies include:
ehlo SEND Send as mail [RFC821]
For an SMTP request of help vrfy,
sendmail might produce:
214-VRFY <recipient>
214- Verify an address. If you want to see what it aliases
214- to, use EXPN instead.
214 End of HELP info
The forms of the HelpFile option are as follows:
O HelpFile=file 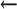 configuration file (V8.7 and later)
-OHelpFile=file
configuration file (V8.7 and later)
-OHelpFile=file 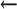 command line (V8.7 and later)
define(`HELP_FILE',`file')
command line (V8.7 and later)
define(`HELP_FILE',`file') 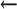 mc configuration (V8.7 and later)
OHfile
mc configuration (V8.7 and later)
OHfile 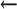 configuration file (deprecated)
-oHfile
configuration file (deprecated)
-oHfile  command line (deprecated)
command line (deprecated)
The argument file is of type
string and can be a full or relative pathname.
Relative names are always relative to the queue directory. If
file is omitted, the name of the help file
defaults to helpfile. If the entire option is
omitted, the name of the help file is undefined. The default for the
mc configuration technique is
/etc/mail/helpfile. SMTP is described in
RFC2821, and ESMTP is described in RFC1869.
The HelpFile option is not safe. If specified from
the command line, it can cause sendmail to
relinquish its special privileges.