A hop is the transmittal of a mail message from
one machine to another. Many hops might be required to deliver a message. The
number of hops is determined by counting the
Received:, Via:,
X400-Received, and Mail-From:
lines in the header of an email message.
The MaxHopCount option tells
sendmail the maximum number of times a message
can be forwarded. When sendmail receives a
message via email, it calculates the hop count. If that count is
above the maximum allowed, it bounces the message back to the sender
with the error:
sendmail: too many hops (17 max)
In this case, 17 is the maximum. Detecting too
many hops is useful in stopping mail
loops—messages being forwarded back and forth
between two machines.
The forms of the MaxHopCount option are as follows:
O MaxHopCount=hops 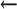 configuration file (V8.7 and later)
-OMaxHopCount=hops
configuration file (V8.7 and later)
-OMaxHopCount=hops 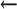 command line (V8.7 and later)
define(`confMAX_HOP',hops)
command line (V8.7 and later)
define(`confMAX_HOP',hops) 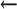 mc configuration (V8.7 and later)
Ohhops
mc configuration (V8.7 and later)
Ohhops 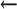 configuration file (deprecated)
-ohhops
configuration file (deprecated)
-ohhops  command line (deprecated)
command line (deprecated)
The hops argument is of type
numeric. If hops is
missing, the value becomes zero and causes all mail to fail with the
error:
sendmail: too many hops (0 max)
If the entire MaxHopCount option is missing,
hops defaults to 25. A good value is 50 or
more (RFC2821, Section 6.2, suggests 100). This allows mail to follow
a fairly long route through many machines (as it could with UUCP) but
still catches and bounces mail caught in a loop between two machines.
The MaxHopCount option should not be confused with
the -h command-line switch (-h). The MaxHopCount option
specifies the maximum number of hops allowed, whereas the
-h command-line switch presets the (beginning) hop
count for a given email message.
The MaxHopCount option is not safe. If specified
from the command line, it can cause sendmail to
relinquish its special privileges.