When a client's site connects to the server, the
server can offer authentication by presenting the AUTH keyword,
followed by authentication mechanisms supported:
250-host.domain Hello some.domain, pleased to meet you
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-PIPELINING
250-8BITMIME
250-SIZE
250-DSN
250-ETRN
250-AUTH DIGEST-MD5 CRAM-MD5 KERBEROS-V4 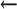 note this line
250-DELIVERBY
250 HELP
note this line
250-DELIVERBY
250 HELP
If the connecting site wishes to authenticate itself, it replies with
an AUTH command indicating the desired mechanism:
AUTH CRAM-MD5
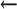 authentication challenge here
authentication challenge here
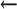 authentication reply here
235 Authentication successful.
authentication reply here
235 Authentication successful. 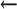 server replies
server replies
This interaction automatically establishes an authenticated stream
using the CRAM-MD5 method.
If you wish to turn off additional encryption in SASL when STARTTLS
is already encrypting the communication, you do so by defining this
AuthMaxBits option. When set, this option limits
the maximum encryption strength for the security layer in SMTP AUTH.
When not set (the default) encryption strength is essentially
unlimited. The AuthMaxBits option is used like
this:
O AuthMaxBits=limit 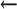 configuration file (V8.12 and later)
-OAuthMaxBits=limit
configuration file (V8.12 and later)
-OAuthMaxBits=limit 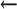 command line (V8.12 and later)
define(`confAUTH_MAX_BITS', `limit')
command line (V8.12 and later)
define(`confAUTH_MAX_BITS', `limit')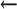 mc configuration (V8.12 and later)
mc configuration (V8.12 and later)
Here, limit is the maximum number of bits in the
keylength. The existing encryption strength is taken into account
when choosing an algorithm for the security layer. For example, if
STARTTLS is used and the symmetric cipher is DES, the keylength (in
bits) will be 168. By setting this option to:
define(`confAUTH_MAX_BITS', `168')
any encryption in SASL will be disabled.
The AuthMaxBits option is not safe. If specified
from the command line, it can cause sendmail to
relinquish its special privileges.