제 3 회 리눅스 공동체 세미나 j 세션
posix 멀티 쓰레딩을 이용한 간단한 체팅서버 만들기!

이인호
c언어는 알지만 네트워크 프로그래밍은 해본 적이 없으신 분
간단한 체팅 서버를 만들어 봅니다
posix thread를 이용한 멀티쓰레딩 프로그래밍을 익히는데 중점을 둡니다
그리고 네트워크 프로그램을 만드는 방법도 간략히 설명합니다
|
|
제 3 회 리눅스 공동체 세미나 j 세션 |
|
|
posix 멀티 쓰레딩을 이용한 간단한 체팅서버 만들기! |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
이인호 |
||
|
c언어는 알지만 네트워크 프로그래밍은 해본 적이 없으신 분 간단한 체팅 서버를 만들어 봅니다 posix thread를 이용한 멀티쓰레딩 프로그래밍을 익히는데 중점을 둡니다 그리고 네트워크 프로그램을 만드는 방법도 간략히 설명합니다 |
||
posix 멀티 쓰레딩을 이용한 간단한 체팅서버 만들기! 361
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tcp 프로그래밍의 기본
인터넷 프로그래밍에 많이 쓰는 소켓 프로그래밍에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 통신 방법에는 '연결 지향형' 과 '비연결 지향형' 이 있습니다. '연결 지향형(connection-oriented)' 과 '비연결 지향형(connectionless)'의 차이점은 인증(accept) 과정을 거치느냐 아니냐 하는 차이입니다. '연결 지향형'은 '1:1 통신' 과 비슷한 방법이라고 생각하시면 됩니다. '비연결 지향형'은 인증과정을 거치지 않습니다. 따라서 한 포트에 다수의 클라이언트가 정보를 보낼 수 있으나 통신의 정확성이 떨어지는 단점이 있습니다. 체팅 서버는 '연결 지향형'을 사용해서 만들어 보겠습니다.
1) 서버 프로그래밍
서버에서 연결하는 절차는 다음과 같습니다.
·socket();
소켓 디스크립터를 할당해 줍니다.
·bind();
소켓 디스크립터를 port와 연결해 줍니다.
·listen();
최대로 허용하는 유저수를 설정합니다.
·accept();
연결을 승인합니다. 또, 서버는 read()를 이용해서 데이터를 읽어오고, write()를 이용해서 데이터를 전송합니다.
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
domain은 프로토콜 형태를 정합니다. af_unix와 af_inet이 있는데 af_unix는 같은 호스트 내에서만 쓰는 것이고, af_inet은 다른 호스트에서도 쓸 수 있습니다.
type은 연결지향인지, 비연결 지향인지를 정합니다. 연결지향은 sock_stream, 비연결 지향은 sock_dgram입니다.
protocol은 특정 프로토콜을 지정합니다. 보통은 0입니다.(하나 밖에 없으므로...)
int bint(int s, const struct sockaddr *address, size_t address_len);
s에는 socket에서 리턴되는 값을 넣어줍니다.
address는 ...
struct sockaddr_in {
short sin_family;
u_short sin_port;
struct in_addr sin_addr;
char sin_zero[8];
};
sin_family는 af_inet으로 합니다. sin_port는 사용할 port번호입니다. sin_addr은 모든 호스트에서의 접속을 허용하기 위해 inaddr_any로 합니다.
address_len은 *address의 사이즈를 지정해 줍니다.
int listen(int s, int backlog);
backlog는 얼마나 많은 연결을 한꺼번에 허용할 것인지 정합니다.
int accept(int s, struct sockaddr *address, int *address_len);
address에는 client의 정보를 담고, address_len은 버퍼의 크기(struct sockaddr의 크기)를 넣어줍니다.
예제1) client와 연결 한 후 이름을 물어보고 ``hello! ''를 출력하는 프로그램 라는 메시지를 출력하고 종료하는 프로그램
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
main() {
int sockfd,fd,clilen,nsize;
struct sockaddr_in addr,cliaddr;
char buf[128];
sockfd = socket(af_inet,sock_stream,0);
addr.sin_family=af_inet;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any);
addr.sin_port = htons(1000);
bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(addr));
listen(sockfd,5);
clilen = sizeof(cliaddr);
fd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cliaddr, &clilen);
if(fd<0) {
perror("accept failed");
return 0;
}
nsize = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
write(fd,"hello",5);
write(fd,buf,nsize);
close(fd);
close(sockfd);
}
hton*, ntoh* 함수들...
hton* 함수들을 사용하는 이유는 호스트 컴퓨터와 네트워크 사이에 바이트 오더링 (byte ordering)이 다를 수 있기 때문입니다. 예를들어 0x3130이란 숫자를 저장할 때, 어떤 시스템은 0x3130 이라 저장하고 어떤 시스템은 0x3031 로 뒤집어서 저장을 하기도 합니다. 네트워크 상에서는 같은 바이트 오더링을 사용해야 하기 때문에 hton* 류의 함수를 사용합니다. hton* 은 호스트의 바이트 오더링을 네트워크 바이트 오더링으로, ntoh* 는 네트워크의 바이트 오더링을 호스트의 바이트 오더링으로 바꿔 줍니다. linux에서는 안 써도 되는 듯 합니다.
2) 클라이언트 프로그래밍
클라이언트 프로그램의 순서는 다음과 같습니다.
·socket();
서버와 같습니다.
·connect();
서버와 연결을 합니다.
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect(int s, struct sockaddr *serv_addr, int addrlen);
s는 socket();에서 얻은 소켓 디스크립터. serv_addr은 연결할 서버를 지정해 줍니다.
예제1과 같은 서버를 사용한다면 여러 클라이언트들이 동시에 서버에 접속을 할 수 없습니다. 이래서는 체팅서버를 만들 수 없겠죠. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해서는 두가지 방법이 있는데...
·fork()를 이용해서 자식 프로세서를 만든다.
·thread 여러개를 만들어 사용한다.
저는 thread를 추천합니다. 더 간편하기 때문이죠. 속도도 더 빠르고, java에서 사용하는 방법이기도 합니다. (저는 멀티쓰레딩을 java에서 처음 접했습니다.) 또한 전역 변수를 공유 할 수 있어서 간편합니다.
thread?
thread란 "프로그램의 흐름" 이란 뜻입니다.
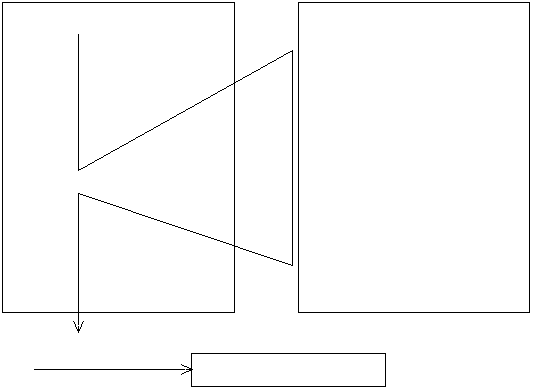
위의 경우는 하나의 쓰레드 만을 쓰는 경우입니다. 멀티쓰레드는 말 그대로 쓰레드를 여러 개 만드는 것입니다.
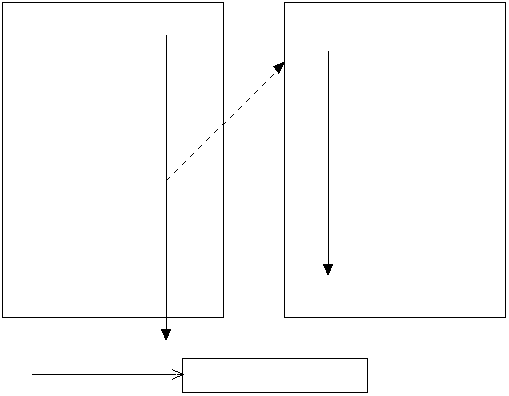
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *tid,const pthread_attr_t *attr, void * ( * start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
pthread_create 는 쓰레드를 하나 생성합니다. tid 는 쓰레드의 id입니다. attr은 쓰레드의 속성을 지정해줍니다. 디폴트로 할려면 null. start_routine 은 함수를 지정해 줍니다. start_routine은 arg를 리턴값은 void입니다.
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_exit(void *value_ptr);
int pthread_join (pthread_t thread, void **value_ptr);
pthread_t pthread_self();
pthread_exit는 쓰레드를 중단시킵니다. value_ptr은 리턴할 값입니다. pthread_join 은 thread가 끝날 때 까지 기다립니다. value_ptr 은 리턴값을 저장할 곧을 지정해 줍니다. pthread_self() 는 쓰레드 자신의 쓰레드 아이디를 넘겨줍니다.
예제) 쓰레드를 만든 후 hello world를 출혁하는 프로그램
#include <pthread.h>
void *hello_world (void *arg)
{
printf ("hello world\n");
return null;
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t hello_id;
int status;
status = pthread_create (&hello_id, null, hello_world, null);
status = pthread_join (hello_id, null);
return 0;
}
채팅 서버를 만들자!
채팅 서버 소스
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxuser 30
int tid;
const char welcome[] = "welcome to cph]['s chating server\n";
const char nick[] = "enter your nickname please?\n\r";
int ulist[maxuser];
int sockfd;
static int ct=0;
void *th(void *arg) {
int sock;
char buf[300];
int nrd,i;
int id;
char nik[80];
id = ct;
ct++;
sock = *((int *)arg);
ulist[id] = sock;
write(sock,nick,sizeof(nick));
read(sock,nik,300);
while(1) {
nrd = read(sock,buf,300);
// printf("%i\n",nrd);
if(((buf[0]=='q')&&(buf[1]=='!'))||(nrd==0)) {
break;
}
for(i=0;i<ct;i++) {
write(ulist[i],nik,strlen(nik)-2);
write(ulist[i]," : ",3);
write(ulist[i],buf,nrd);
}
}
for(i=id;i<ct;i++) {
ulist[i]=ulist[i+1];
}
ct--;
// printf("ct is : %i\n",ct);
close(sock);
// printf("good bye!\n");
}
void catch_ctrl_c(int signo) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<ct;i++) {
close(ulist[i]);
}
close(sockfd);
raise(9);
}
main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
int new_sockfd ,clilen,childpid,i,flag;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr, serv_addr;
int port = 7250;
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = catch_ctrl_c;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(sigint, &act, null);
printf("cph]['s very simple chating server beta 0.0.1\n");
if(argc==2) {
port = atoi(argv[1]);
}
sockfd = socket(af_inet,sock_stream,0);
// bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = af_inet;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
if(bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr,sizeof(serv_addr))<0) {
perror("server bind error");
exit(1);
}
listen(sockfd, maxuser);
while(1) {
clilen = sizeof(cli_addr);
if((new_sockfd = accept(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *) &cli_addr, &clilen))<0) {
perror("accept error\n");
exit(1);
}
// printf("ok! new_sockfd = %i\n",new_sockfd);
pthread_create(&tid,0,th,(void *)&new_sockfd);
}
}
mutex
멀티 쓰레드 프로그램을 만들 때의 문제점 중의 하나는 메모리를 공유할 때에 순서 없이 제어를 하다보면 엉망이 되어 버리는 것입니다. 이런 일을 해결하기 위한 것에는 mutex 와 condition variable, 그리고 전통적인 방법인 semaphore가 있습니다.
mutex 는 "mutual" 과 "exclusion" 의 합성어입니다. 이 메커니즘의 요점은 한 메모리에 여러 쓰레드가 동시에 제어할 수 없게 만드는 것입니다. mutex 는 pthread_mutex_lock(); 으로 다른 쓰레드의 제어를 막고 pthread_mutex_unlock(); 으로 다른 쓰레드의 제어를 허용해야 합니다.
mutex에 의해 보호되는 변수들은 반드시 pthread_mutex_lock()을 한 후에 제어를 해야 합니다.
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t m);
pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t m);
pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t m);
pthread_mutex_lock() 은 mutex를 lock하기 위해 시도합니다. 만약 다른 쓰레드가 mutex를 lock 한 상태라면 unlock 되기까지 기다립니다. pthread_mutex_trylock() 또한 lock() 과 비슷하지만 unlock 되기까지 기다리지 않고 lock 이 안되었으면 을 리턴 합니다.
pthread_mutex_t 는 mutex의 정보를 담고 있는 자료형입니다. pthread_mutex_initialize 라는 매크로를 이용해서 초기화 할 수도 있고, pthread_mutex_init()를 통해 초기화 할 수 있습니다. 동적으로 하려하거나, 특수한 속성을 부여하려면 pthread_mutex_init()를 사용합니다.
mutex를 사용한 채팅 서버
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxuser 30
int tid;
const char welcome[] = "welcome to cph]['s chating server\n";
const char nick[] = "enter your nickname please?\n\r";
int ulist[maxuser];
pthread_mutex_t ulist_mutex = pthread_mutex_initializer;
pthread_mutex_t arg_mutex = pthread_mutex_initializer;
int sockfd,commfd;
static int ct=0;
void *th(void *arg) {
char buf[300];
int nrd,i;
int id;
char nik[80];
int *sc,sock;
sc = (int *)arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&arg_mutex);
sock = sc[0];
pthread_mutex_unlock(&arg_mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&ulist_mutex);
id = ct;
ct++;
ulist[id] = sock;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&ulist_mutex);
write(sock,nick,sizeof(nick));
read(sock,nik,300);
while(1) {
nrd = read(sock,buf,300);
// printf("%i\n",nrd);
if(((buf[0]=='q')&&(buf[1]=='!'))||(nrd==0)) {
break;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&ulist_mutex);
for(i=0;i<ct;i++) {
write(ulist[i],nik,strlen(nik)-2);
write(ulist[i]," : ",3);
write(ulist[i],buf,nrd);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&ulist_mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&ulist_mutex);
for(i=id;i<ct;i++) {
ulist[i]=ulist[i+1];
}
ct--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&ulist_mutex);
// printf("ct is : %i\n",ct);
close(sock);
// printf("good bye!\n");
}
void catch_ctrl_c(int signo) {
int i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&ulist_mutex);
printf("ok\n");
for(i=0;i<ct;i++) {
close(ulist[i]);
}
ct = 0;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&ulist_mutex);
close(commfd);
close(sockfd);
raise(9);
}
main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
int new_sockfd ,clilen,childpid,i,flag;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr, serv_addr;
int port = 7250;
int fa[1];
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = catch_ctrl_c;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(sigint, &act, null);
printf("cph]['s very simple chating server beta 0.0.1\n");
if(argc==2) {
port = atoi(argv[1]);
}
sockfd = socket(af_inet,sock_stream,0);
// bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = af_inet;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
if(bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr,sizeof(serv_addr))<0) {
perror("server bind error");
exit(1);
}
commfd = listen(sockfd, maxuser);
while(1) {
clilen = sizeof(cli_addr);
if((new_sockfd = accept(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *) &cli_addr, &clilen))<0) {
perror("accept error\n");
exit(1);
}
fa[0] = new_sockfd;
pthread_create(&tid,0,th,(void *)fa);
}
}
condition variable
condition variable 는 변수의 사용과 관련된 일종의 통신 메커니즘입니다. 공유하는 메모리를 제어하고자 하는 쓰레드가 메모리가 필요한 조건에 맞지를 않을 때 (예를 들어 큐가 꽉 찾을 때) 쓰레드는 조건의 상태가 바뀌기를 기다립니다. 다른 쓰레드가 메모리가 바뀌었음을 알려주면 (signal) 사용을 기다리던 쓰레드는 다시 조건을 검사하고, 조건이 맞으면 사용합니다.
thread a :
1 pthread_mutex_lock(&mu);
2 while(x != y) pthread_cond_wait(&v,&mu);
3 /* x와 y에 관한 일 */
4 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu);
위의 예제에서 쓰레드가 작업을 계속하기 위해서 필요한 조건은 x == y입니다. (주의 : while 문이므로 x != y 가 거짓일 때 까지 기다립니다.) thread a 는 mutex mu를 잠그고 조건을 검사한 후 신호를 기다립니다. 신호를 받을 때 까지는 3번 행을 실행하지 않습니다. 신호를 기다릴 때는 while 이나 for 등의 반복문을 사용해야 합니다. if 문은 한 번 밖에 기다리지 않으므로 부적합합니다.
thread b :
1 pthread_mutex_lock(&mu);
2 x++;
3 pthread_cond_signal(&v);
4 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu);
broadcast 와 signal
만약에 대기중인 쓰레드들이 각자 다른 조건을 원하고 있다면(예를 들어 쓰레드 a는 큐가 꽉 차기를, 쓰레드 b는 큐에 데이터가 하나도 없기를) broadcast를 사용해 줍니다. 만약 그렇지 않다면 signal을 사용하는 것이 더 능률적입니다.
mutex와 같이 사용
condition value는 mutex와 같이 사용합니다. mutex를 lock 하고 대기를 하게 되면 대기 할 때 mutex를 풀어줍니다. 다시 신호를 받고 return 할 때에는 mutex를 lock 한 상태로 돌아오게 됩니다. 쓰레드가 대기를 할 때에는 반드시 mutex가 잠겨 있어야 합니다. 만약 그렇지 않다면 wait 하는 과정에서 다른 쓰레드와 겹쳐져서 오류가 생길 수도 있습니다.
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_cond_init();
pthread_cond_t를 초기화합니다. 매크로 pthread_cond_initializer도 있습니다.
pthread_cond_signal();
wait를 하고있는 하나의 쓰레드에 신호를 줍니다.
pthread_cond_wait();
신호를 기다립니다.
pthread_cond_broadcast();
기다리고 있는 모든 쓰레드에 신호를 줍니다.
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef struct my_struct_tag {
pthread_mutex_t mutex; /* protects access to value */
pthread_cond_t cond; /* signals change to value */
int value; /* access protected by mutex */
} my_struct_t;
my_struct_t data = {
pthread_mutex_initializer, pthread_cond_initializer, 0};
int hibernation = 1; /* default to 1 second */
/*
* thread start routine. it will set the main thread's predicate
* and signal the condition variable.
*/
void *
wait_thread (void *arg)
{
int status;
sleep (hibernation);
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&data.mutex);
data.value = 1; /* set predicate */
status = pthread_cond_signal (&data.cond);
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&data.mutex);
return null;
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
int status;
pthread_t wait_thread_id;
struct timespec timeout;
/*
* if an argument is specified, interpret it as the number
* of seconds for wait_thread to sleep before signaling the
* condition variable. you can play with this to see the
* condition wait below time out or wake normally.
*/
if (argc > 1)
hibernation = atoi (argv[1]);
/*
* create wait_thread.
*/
status = pthread_create (&wait_thread_id, null, wait_thread, null);
/*
* wait on the condition variable for 2 seconds, or until
* signaled by the wait_thread. normally, wait_thread
* should signal. if you raise "hibernation" above 2
* seconds, it will time out.
*/
timeout.tv_sec = time (null) + 2;
timeout.tv_nsec = 0;
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&data.mutex);
while (data.value == 0) {
status = pthread_cond_timedwait (
&data.cond, &data.mutex, &timeout);
if (status == etimedout) {
printf ("condition wait timed out.\n");
break;
}
}
if (data.value != 0)
printf ("condition was signaled.\n");
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&data.mutex);
return 0;
}
thread-specific data
보통의 프로그램에서 쓰는 전역변수 처럼, 한 쓰레드 안아서 공유할 수 있는 변수를 만들 수 있습니다. thread-specific data는 공유할 변수의 포인터를 기억 했다가 돌려 줍니다. 프로그램에서는 하나의 thread-specific key 만을 사용하지만 각각의 쓰레드 마다 key 가 가리키는 주소가 다르게 됩니다. 따라서 각각의 쓰레드는 쓰레드만의 전역 변수를 가질 수 있게 됩니다.
pthread_key_t key;
int pthread_key_create(pthread_key_y *key, void (*destructor)(void *));
int pthread_key_delete(pthread_key_t key);
int pthread_setspecific(pthread_key_t key, const void *value);
void *pthread_getspecific (pthread_key_t key);
key 는 thread-specific key를 저장하는 구조체입니다. pthread_key_create는 키 하나를 destructor 와 함께 만듭니다. pthread_key_delete 는 key를 삭제합니다. pthread_setspecific 은 key 가 어떤 value를 지정하게 할 것인가를 정하게 합니다. pthread_getspecific 은 key 값에 해당하는 변수의 주소를 얻어 옵니다.
예제) thread-specific key
#include <pthread.h>
/*
* structure used as the value for thread-specific data key.
*/
typedef struct tsd_tag {
pthread_t thread_id;
char *string;
} tsd_t;
pthread_key_t tsd_key; /* thread-specific data key */
pthread_once_t key_once = pthread_once_init;
/*
* one-time initialization routine used with the pthread_once
* control block.
*/
void once_routine (void)
{
int status;
printf ("initializing key\n");
status = pthread_key_create (&tsd_key, null);
}
/*
* thread start routine that uses pthread_once to dynamically
* create a thread-specific data key.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
tsd_t *value;
int status;
status = pthread_once (&key_once, once_routine);
value = (tsd_t*)malloc (sizeof (tsd_t));
status = pthread_setspecific (tsd_key, value);
printf ("%s set tsd value %p\n", arg, value);
value->thread_id = pthread_self ();
value->string = (char*)arg;
value = (tsd_t*)pthread_getspecific (tsd_key);
printf ("%s starting...\n", value->string);
sleep (2);
value = (tsd_t*)pthread_getspecific (tsd_key);
printf ("%s done...\n", value->string);
return null;
}
void main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread1, thread2;
int status;
status = pthread_create (
&thread1, null, thread_routine, "thread 1");
status = pthread_create (
&thread2, null, thread_routine, "thread 2");
pthread_exit (null);
}
destructor 예제
#include <pthread.h>
/*
* structure used as value of thread-specific data key.
*/
typedef struct private_tag {
pthread_t thread_id;
char *string;
} private_t;
pthread_key_t identity_key; /* thread-specific data key */
pthread_mutex_t identity_key_mutex = pthread_mutex_initializer;
long identity_key_counter = 0;
/*
* this routine is called as each thread terminates with a value
* for the thread-specific data key. it keeps track of how many
* threads still have values, and deletes the key when there are
* no more references.
*/
void identity_key_destructor (void *value)
{
private_t *private = (private_t*)value;
int status;
printf ("thread \"%s\" exiting...\n", private->string);
free (value);
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&identity_key_mutex);
identity_key_counter--;
if (identity_key_counter <= 0) {
status = pthread_key_delete (identity_key);
printf ("key deleted...\n");
}
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&identity_key_mutex);
}
/*
* helper routine to allocate a new value for thread-specific
* data key if the thread doesn't already have one.
*/
void *identity_key_get (void)
{
void *value;
int status;
value = pthread_getspecific (identity_key);
if (value == null) {
value = malloc (sizeof (private_t));
if (value == null)
errno_abort ("allocate key value");
status = pthread_setspecific (identity_key, (void*)value);
}
return value;
}
/*
* thread start routine to use thread-specific data.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
private_t *value;
value = (private_t*)identity_key_get ();
value->thread_id = pthread_self ();
value->string = (char*)arg;
printf ("thread \"%s\" starting...\n", value->string);
sleep (2);
return null;
}
void main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread_1, thread_2;
private_t *value;
int status;
/*
* create the tsd key, and set the reference counter to
* the number of threads that will use it (two thread_routine
* threads plus main). this must be done before creating
* the threads! otherwise, if one thread runs the key's
* destructor before any other thread uses the key, it will
* be deleted.
*
* note that there's rarely any good reason to delete a
* thread-specific data key.
*/
status = pthread_key_create (&identity_key, identity_key_destructor);
identity_key_counter = 3;
value = (private_t*)identity_key_get ();
value->thread_id = pthread_self ();
value->string = "main thread";
status = pthread_create (&thread_1, null,
thread_routine, "thread 1");
status = pthread_create (&thread_2, null,
thread_routine, "thread 2");
pthread_exit (null);
}
fork();
멀티쓰레드 프로그램에서 fork();를 사용할 경우 그 때의 행동을 pthread_atfork()로 정의할 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 prepare에서는 모든 mutex를 잠그고, parent에서의 모두 unlock 합니다.
(주의) 멀티 쓰레드 프로그램에서는 fork(); 사용을 피하는 것이 좋습니다.
<예제 fork()를 사용하는 예>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t self_pid; /* pid of current process */
pthread_mutex_t mutex = pthread_mutex_initializer;
void fork_prepare (void)
{
int status;
/*
* lock the mutex in the parent before creating the child,
* to ensure that no other thread can lock it (or change any
* associated shared state) until after the fork completes.
*/
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&mutex);
}
/*
* this routine will be called after executing the fork, within
* the parent process
*/
void fork_parent (void)
{
int status;
/*
* unlock the mutex in the parent after the child has been created.
*/
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex);
}
/*
* this routine will be called after executing the fork, within
* the child process
*/
void fork_child (void)
{
int status;
/*
* update the file scope "self_pid" within the child process, and unlock
* the mutex.
*/
self_pid = getpid ();
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex);
}
/*
* thread start routine, which will fork a new child process.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
pid_t child_pid;
int status;
child_pid = fork ();
/*
* lock the mutex -- without the atfork handlers, the mutex will remain
* locked in the child process and this lock attempt will hang (or fail
* with edeadlk) in the child.
*/
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&mutex);
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex);
printf ("after fork: %d (%d)\n", child_pid, self_pid);
if (child_pid != 0) {
waitpid (child_pid, (int*)0, 0);
}
return null;
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t fork_thread;
int atfork_flag = 1;
int status;
if (argc > 1)
atfork_flag = atoi (argv[1]);
if (atfork_flag) {
status = pthread_atfork (fork_prepare, fork_parent, fork_child);
}
self_pid = getpid ();
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&mutex);
/*
* create a thread while the mutex is locked. it will fork a process,
* which (without atfork handlers) will run with the mutex locked.
*/
status = pthread_create (&fork_thread, null, thread_routine, null);
sleep (5);
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex);
status = pthread_join (fork_thread, null);
return 0;
}
stdio
pthread 에서는 stdio를 thread safe 로 정하고 있습니다. 그러나 stdio를 여러 쓰레드가 쓸려고 달려들 경우 (stdio 뿐만 아니라 대부분의 file * ) 이상한 결과가 나올 수 있습니다. 이 것을 막기 위한 함수가 flockfile(file *); 과 funlockfile(file *);, ftrylockfile(file *) 입니다. 두 가지가 작동하는 원리는 mutex와 크게 다르지 않습니다. 락을 걸때는 입력 스트림을 먼저 lock 해 주고, 풀때는 그 반대로 하도록 posix 문서에서 권고하고 있습니다.
<예제> stdio의 lock 과 unlock
#include <pthread.h>
/*
* this routine writes a prompt to stdout (passed as the thread's
* "arg"), and reads a response. all other i/o to stdin and stdout
* is prevented by the file locks until both prompt and fgets are
* complete.
*/
void *prompt_routine (void *arg)
{
char *prompt = (char*)arg;
char *string;
int len;
string = (char*)malloc (128);
flockfile (stdin);
flockfile (stdout);
printf (prompt);
if (fgets (string, 128, stdin) == null)
string[0] = '\0';
else {
len = strlen (string);
if (len > 0 && string[len-1] == '\n')
string[len-1] = '\0';
}
funlockfile (stdout);
funlockfile (stdin);
return (void*)string;
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread1, thread2, thread3;
char *string;
int status;
status = pthread_create (
&thread1, null, prompt_routine, "thread 1> ");
status = pthread_create (
&thread2, null, prompt_routine, "thread 2> ");
status = pthread_create (
&thread3, null, prompt_routine, "thread 3> ");
status = pthread_join (thread1, (void**)&string);
printf ("thread 1: \"%s\"\n", string);
free (string);
status = pthread_join (thread2, (void**)&string);
printf ("thread 1: \"%s\"\n", string);
free (string);
status = pthread_join (thread3, (void**)&string);
printf ("thread 1: \"%s\"\n", string);
free (string);
return 0;
}
cancellation
cancellation은 현재 실행중인 쓰레드를 중지시킵니다. 프로세서에게 sigint나 sigkill의 시그널을 주는 것과 같다고 생각하시면 됩니다. cancellation 은 두 가지 방식이 있는데 deferred와 비동기적 방법이 있습니다. deferred방식으로 cancellation을 할 경우에는 쓰레드가 pthread_testcancel() 하기 전에는 쓰레드가 멈추지 않습니다. 반면 비동기적 방법은 쓰레드가 그 즉시 멈춥니다. 꼭 필요하지 않은 경우에는 cancellation을 쓰는 것 보다는 pthread_join을 써서 쓰레드가 끝날 때 까지 기다리는 것이 더 안전합니다. 단, 무한루프를 도는 쓰레드를 만들어서 작업을 하다가 인위적으로 마치게 하는 프로그램 같은 경우에는 유용할 수 있습니다.
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);
int pthread_setcanceltype(int type, int *oldtype);
void pthread_testcancel(void);
void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routin)(void *), void *arg);
void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
pthread_cancel 은 thread의 실행을 멈추게 합니다. pthread_setcancelstate 는 취소가 불가능하게 할 건지(pthread_cancel_disable), 가능 하게 할 건지(pthread_cancel_enable)를 정합니다. state 에는 가능, 불가능 여부를, oldstate에는 설정 이전의 상태를 저장해 줍니다. pthread_setcanceltype는 위에서 설명한 cancel 형태를 정해 줍니다. default 는 deferred입니다. pthread_cancel_deferred, pthread_cancel_asynchronous. testcancel 은 위에서 설명한 대로입니다. cleanup 은 취소가 될 때 실행할 함수들을 지정합니다. cleanup_push 는 쓰레드가 취소가 될 때 실행할 함수(예를 들면, mutex를 unlock 하는..)를 스택에 저장합니다. cleanup_pop은 스택에서 빼냅니다. execute 가 0이 아니면, 그 함수를 실행하고 끝냅니다.
#include <pthread.h>
static int counter;
/*
* loop until cancelled. the thread can be cancelled only
* when it calls pthread_testcancel, which it does each 1000
* iterations.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
for (counter = 0; ; counter++)
if ((counter % 1000) == 0) {
pthread_testcancel ();
}
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread_id;
void *result;
int status;
status = pthread_create (
&thread_id, null, thread_routine, null);
sleep (2);
status = pthread_cancel (thread_id);
status = pthread_join (thread_id, &result);
if (result == pthread_canceled)
printf ("thread cancelled at iteration %d\n", counter);
else
printf ("thread was not cancelled\n");
return 0;
}
deferred
deferred로 하는 경우에는 `cancel 명령이 들어왔다' 는 것이 전달이 되고 testcancel을 하게 되면 thread가 cancel 됩니다. cancel 명령은 단순한 시그널과는 달리 반드시 그 쓰레드가 cancel 이 되어야 합니다. 곧 cancel 이 들어왔어도 그냥 지나칠 수는 없습니다.
일반적으로 unix 에서는 testcancel 외에도 sleep, mutex_lock 등의 함수가 testcancel 과 같은 작용을 합니다. mutex를 잠근 상태에서 쓰레드가 cancel 될 경우에는 그 mutex를 잠그려고 하는 다른 쓰레드들은 데드락에 걸리게 되고, 결국 프로그램이 제대로 돌아가지 않습니다. 이런 일을 피하기 위해서 cleanup을 사용하던지 cancel 속성을 disable 로 바꿔서 cancel 이 안되게 것이 좋습니다.
비동기적
비동기적 방법은 언제든지 쓰레드를 취소할 수 있습니다. 따라서, 정상적으로 종료하기 위해서는 중요한 부분에서는 취소가 불가능하게 설정하거나, cleanup을 설정하는 것이 좋습니다. 비동기적 취소 방법이 설정되어 있는 상태에서는, 리소스를 요구하는 함수들을 호출하는 것도 피해야 합니다. 예를 들어 malloc 가 실행 중에 취소 되는 경우에는 heap에서 메모리를 할당 받았지만 주소를 넘겨주지 못하고 끝나버리게 됩니다. 그렇게 된다면 그 프로그램에서는 할당을 어디에 받았는지 알 수 없게 되어 문제가 됩니다.
따라서, 함수를 호출할 때에는 그 함수가 안전한지를 반드시 알아본 후에 호출을 해야 합니다. pthread 함수들 중에서 비동기적인 방법에 안전한 함수는 pthread_cancel(), pthread_setcancelstate, pthread_setcanceltype 뿐입니다.
<예제> deffered
#include <pthread.h>
static int counter;
/*
* thread start routine.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
int state;
int status;
for (counter = 0; ; counter++) {
/*
* each 755 iterations, disable cancellation and sleep
* for one second.
*
* each 1000 iterations, test for a pending cancel by
* calling pthread_testcancel().
*/
if ((counter % 755) == 0) {
status = pthread_setcancelstate (
pthread_cancel_disable, &state);
sleep (1);
status = pthread_setcancelstate (
state, &state);
} else
if ((counter % 1000) == 0)
pthread_testcancel ();
}
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread_id;
void *result;
int status;
status = pthread_create (
&thread_id, null, thread_routine, null);
sleep (2);
status = pthread_cancel (thread_id);
status = pthread_join (thread_id, &result);
if (result == pthread_canceled)
printf ("thread cancelled at iteration %d\n", counter);
else
printf ("thread was not cancelled\n");
return 0;
}
<예제> 비동기적
#include <pthread.h>
#define size 10 /* array size */
static int matrixa[size][size];
static int matrixb[size][size];
static int matrixc[size][size];
/*
* loop until cancelled. the thread can be cancelled at any
* point within the inner loop, where asynchronous cancellation
* is enabled. the loop multiplies the two matrices matrixa
* and matrixb.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
int cancel_type, status;
int i, j, k, value = 1;
/*
* initialize the matrices to something arbitrary.
*/
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (j = 0; j < size; j++) {
matrixa[i][j] = i;
matrixb[i][j] = j;
}
while (1) {
/*
* compute the matrix product of matrixa and matrixb.
*/
status = pthread_setcanceltype (
pthread_cancel_asynchronous,
&cancel_type);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (j = 0; j < size; j++) {
matrixc[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < size; k++)
matrixc[i][j] += matrixa[i][k] * matrixb[k][j];
}
status = pthread_setcanceltype (
cancel_type,
&cancel_type);
/*
* copy the result (matrixc) into matrixa to start again
*/
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
matrixa[i][j] = matrixc[i][j];
}
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread_id;
void *result;
int status;
status = pthread_create (
&thread_id, null, thread_routine, null);
sleep (1);
status = pthread_cancel (thread_id);
status = pthread_join (thread_id, &result);
if (status != 0)
err_abort (status, "join thread");
if (result == pthread_canceled)
printf ("thread cancelled\n");
else
printf ("thread was not cancelled\n");
return 0;
}
<예제> cleanup
#include <pthread.h>
#define threads 5
/*
* control structure shared by the test threads, containing
* the synchronization and invariant data.
*/
typedef struct control_tag {
int counter, busy;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cv;
} control_t;
control_t control =
{0, 1, pthread_mutex_initializer, pthread_cond_initializer};
/*
* this routine is installed as the cancellation cleanup
* handler around the cancellable condition wait. it will
* be called by the system when the thread is cancelled.
*/
void cleanup_handler (void *arg)
{
control_t *st = (control_t *)arg;
int status;
st->counter--;
printf ("cleanup_handler: counter == %d\n", st->counter);
status = pthread_mutex_unlock (&st->mutex);
}
/*
* multiple threads are created running this routine (controlled
* by the threads macro). they maintain a "counter" invariant,
* which expresses the number of running threads. they specify a
* nonzero value to pthread_cleanup_pop to run the same
* "finalization" action when cancellation does not occur.
*/
void *thread_routine (void *arg)
{
int status;
pthread_cleanup_push (cleanup_handler, (void*)&control);
status = pthread_mutex_lock (&control.mutex);
control.counter++;
while (control.busy) {
status = pthread_cond_wait (&control.cv, &control.mutex);
}
pthread_cleanup_pop (1);
return null;
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread_id[threads];
int count;
void *result;
int status;
for (count = 0; count < threads; count++) {
status = pthread_create (
&thread_id[count], null, thread_routine, null);
}
sleep (2);
for (count = 0; count < threads; count++) {
status = pthread_cancel (thread_id[count]);
status = pthread_join (thread_id[count], &result);
if (result == pthread_canceled)
printf ("thread %d cancelled\n", count);
else
printf ("thread %d was not cancelled\n", count);
}
return 0;
}
참고한 책/인터넷 사이트
practical unix programming - a guide to concurrency, communication, and multithreading
1997, kay a. robbins/steven robbins
programming with posix threads
david r. butenhof
pthread tutorial <http://www.actcom.co.il/~choo/lupg/tutorials/>
물리적(!) 도움을 주신 분
이 영철