

 |
|
 |
|
Answers Database
JTAG - General description of the TAP controller states.
Record #3203
Product Family: Software 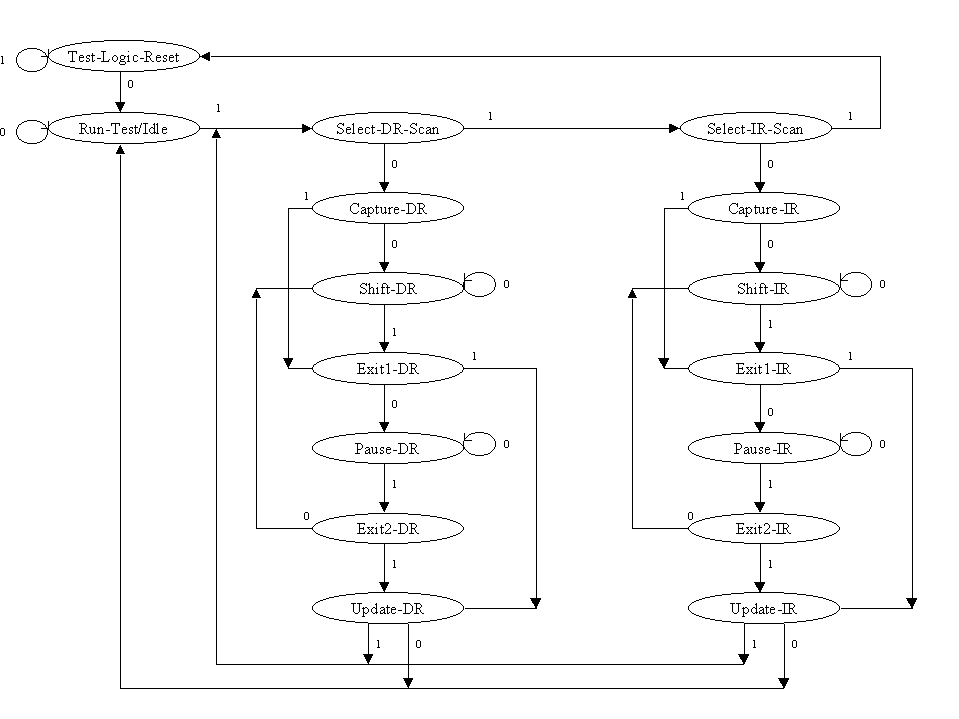 The TAP Controller occurs on the rising edge of TCK. Each state has a different name. The two vertical columns with seven states each represent the Instruction Path and the Data Path. The data registers operate in the states whose names end with "DR" and the instruction register operates in the states whose names end in "IR". The states are identical otherwise. The operation of each state is described below. Test-Logic-Reset All test logic is disabled in this controller state enabling the normal operation of the IC. The TAP controller state machine is designed in such a way that, no matter what the initial state of the controller is, the Test-Logic-Reset state can be entered by holding TMS at high and pulsing TCK five times. This is the reason why the Test Reset (TRST) pin is optional. Run-Test-Idle In this controller state, the test logic in the IC is active only if certain instructions are present. For example, if an instruction activates the self test, then it will be executed when the controller enters this state. The test logic in the IC is idles otherwise. Select-DR-Scan This is a controller state where the decision to enter the Data Path or the Select-IR-Scan state is made. Select-IR-Scan This is a controller state where the decision to enter the Instruction Path is made. The Controller can return to the Test-Logic-Reset state other wise. Capture-IR In this controller state, the shift register bank in the Instruction Register parallel loads a pattern of fixed values on the rising edge of TCK. The last two significant bits are always required to be "01". Shift-IR In this controller state, the instruction register gets connected between TDI and TDO, and the captured pattern gets shifted on each rising edge of TCK. The instruction available on the TDI pin is also shifted in to the instruction register. Exit1-IR This is a controller state where a decision to enter either the Pause-IR state or Update-IR state is made. Pause-IR This state is provided in order to allow the shifting of instruction register to be temporarily halted. Exit2-DR This is a controller state where a decision to enter either the Shift-IR state or Update-IR state is made. Update-IR In this controller state, the instruction in the instruction register is latched in to the latch bank of the Instruction Register on every falling edge of TCK. This instruction also becomes the current instruction once it is latched. Capture-DR In this controller state, the data is parallel loaded in to the data registers selected by the current instruction on the rising edge of TCK. Shift-Dr, Exit1-DR, Pause-DR, Exit2-DR and Update-DR These controller states are similar to the Shift-IR, Exit1-IR, Pause-IR, Exit2-IR and Update-IR states in the Instruction path. End of Record #3203 - Last Modified: 01/10/00 20:12 |

| For the latest news, design tips, and patch information on the Xilinx design environment, check out the Technical Tips! |