 Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++
Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++




Consider the path 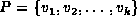 in a directed graph
in a directed graph 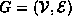 .
.
-
Vertex
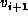 is the successor
of vertex
is the successor
of vertex 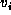 for
for 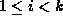 .
Each element
.
Each element 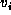 of path P (except the last)
has a successor.
of path P (except the last)
has a successor. -
Vertex
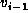 is the predecessor
of vertex
is the predecessor
of vertex 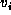 for
for 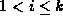 .
Each element
.
Each element 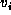 of path P (except the first)
has a predecessor.
of path P (except the first)
has a predecessor. -
A path P is called a simple path if and only if
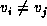 for all i and j such that
for all i and j such that 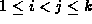 .
However, it is permissible for
.
However, it is permissible for 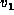 to be the same as
to be the same as 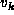 in a simple path.
in a simple path. -
A cycle is a path P
of non-zero length in which
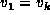 .
The length of a cycle is just the length of the path P.
.
The length of a cycle is just the length of the path P. -
A loop is a cycle of length one.
I.e., it is a path of the form
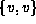 .
. -
A simple cycle
is a path that is both a cycle and simple.
Referring again to graph 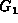 in Figure
in Figure  we find that the path
we find that the path
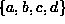 is a simple path of length three.
Conversely, the path
is a simple path of length three.
Conversely, the path 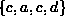 also has length three
but is not simple because vertex c occurs twice in the sequence
(but not at the ends).
The graph contains the path
also has length three
but is not simple because vertex c occurs twice in the sequence
(but not at the ends).
The graph contains the path 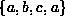 which is a cycle of length three,
as well as
which is a cycle of length three,
as well as 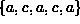 , a cycle of length four.
The former is a simple cycle but the latter is not.
, a cycle of length four.
The former is a simple cycle but the latter is not.




 Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
![]() in a directed graph
in a directed graph ![]() .
.
![]() in Figure
in Figure ![]() we find that the path
we find that the path
![]() is a simple path of length three.
Conversely, the path
is a simple path of length three.
Conversely, the path ![]() also has length three
but is not simple because vertex c occurs twice in the sequence
(but not at the ends).
The graph contains the path
also has length three
but is not simple because vertex c occurs twice in the sequence
(but not at the ends).
The graph contains the path ![]() which is a cycle of length three,
as well as
which is a cycle of length three,
as well as ![]() , a cycle of length four.
The former is a simple cycle but the latter is not.
, a cycle of length four.
The former is a simple cycle but the latter is not.