 Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++
Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++




An undirected graph is a graph in which the nodes are connected by
undirected arcs .
An undirected arc is an edge that has no arrow.
Both ends of an undirected arc are equivalent--there is no head or tail.
Therefore, we represent an edge in an undirected graph
as a set rather than an ordered pair:
Definition (Undirected Graph)
An undirected graph
is an ordered pair 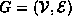 with the following properties:
with the following properties:
-
The first component,
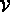 , is a finite, non-empty set.
The elements of
, is a finite, non-empty set.
The elements of 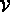 are called the vertices of G.
are called the vertices of G. -
The second component,
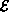 , is a finite set of sets.
Each element of
, is a finite set of sets.
Each element of 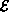 is a set that is comprised of
exactly two (distinct) vertices.
The elements of
is a set that is comprised of
exactly two (distinct) vertices.
The elements of 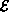 are called the edges of G.
are called the edges of G.
For example, consider the undirected graph 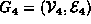 comprised of four vertices and four edges:
comprised of four vertices and four edges:
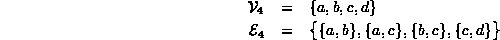
The graph  can be represented
graphically as shown in Figure
can be represented
graphically as shown in Figure  .
The vertices are represented by appropriately labeled circles,
and the edges are represented by lines
that connect associated vertices.
.
The vertices are represented by appropriately labeled circles,
and the edges are represented by lines
that connect associated vertices.
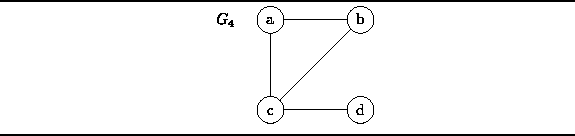
Figure: An Undirected Graph
Notice that because an edge in an undirected graph is a set,
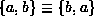 ,
and since
,
and since 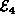 is also a set,
it cannot contain more than one instance of a given edge.
Another consequence of Definition
is also a set,
it cannot contain more than one instance of a given edge.
Another consequence of Definition  is that there cannot be an
edge from a node to itself in an undirected graph
because an edge is a set of size two
and a set cannot contain duplicates.
is that there cannot be an
edge from a node to itself in an undirected graph
because an edge is a set of size two
and a set cannot contain duplicates.




 Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
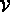 , is a finite, non-empty set.
The elements of
, is a finite, non-empty set.
The elements of 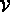 are called the vertices of G.
are called the vertices of G.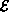 , is a finite set of sets.
Each element of
, is a finite set of sets.
Each element of  is a set that is comprised of
exactly two (distinct) vertices.
The elements of
is a set that is comprised of
exactly two (distinct) vertices.
The elements of  are called the edges of G.
are called the edges of G.
