 Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++
Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++




A variable is a programming language abstraction
that represents a storage location.
A variable has the following attributes:
- name
-
The name of a variable is the label
used to identify a variable in the text of a program.
- address
-
The address of a variable is the
memory address of the storage location(s) occupied by that variable.
The address attribute of a variable
is also known as the l-value because
the l-value of a variable is required when a variable name is used
on the left side of an assignment statement.
- size
-
The size of a variable is the amount
of storage (in bytes) occupied by that variable.
- type
-
The type of a variable determines the set of values
that the variable can have and
the set of operations that can be performed on that variable.
- value
-
The value of a variable is the content
of the memory location(s) occupied by that variable.
(How the contents of the memory locations are interpreted is
determined by the type of the variable).
The value attribute of a variable
is also known as the r-value because
the r-value of a variable is required when a variable name is used
on the right side of an assignment statement.
- lifetime
-
The lifetime of a variable is the
interval of time in the execution of a program
during which a variable is said to exist.
Some variables exist for the entire execution of a program;
some are created and destroyed automatically
during the execution of a program;
and others are explicitly created and destroyed by the programmer.
- scope
-
The scope of a variable is the range
of statements in the text of a program in which that variable
can be referenced.
Consider the C++ variable declaration statement:
int i = 57;
This statement defines a variable
and binds various attributes with that variable.
The name of the variable is i,
the type of the variable is int,
its size is 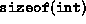 (typically two or four bytes),
and its initial value is 57.
(typically two or four bytes),
and its initial value is 57.
Some attributes of a variable, such its name, type and size,
are bound at compile time.
This is called static binding.
Other attributes of a variable, such as its address and value,
may be bound at run time.
This is called dynamic binding.




 Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1997 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.