Figure: Memory Layout of C++ Variables and Pointers
The C++ statement
int* p;declares a pointer . A pointer is a variable the type of which has the form
Since a pointer is a variable, it has all the attributes of a variable. In particular, it has both an address (l-value) and a value (r-value).
Consider a C++ program that contains the following global variable declarations:
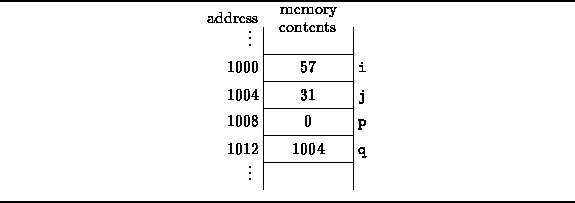
int i = 57; int j = 31; int* p = 0; int* q = (int*) 1004;Suppose the four variables, i, j, p and q, are stored in contiguous memory locations starting at address 1000 as shown in Figure

Figure: Memory Layout of C++ Variables and Pointers
An assignment statement such as
i = j;takes the value (r-value) of j, in this case 31, and stores it in memory at the address (l-value) of i, in this case 1000. Similarly, the assignment
p = q;takes the value of q, in this case 1004, and stores it in memory at the address of p, in this case 1008.