 Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in Java
Data Structures and Algorithms
with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in Java




Section  shows how a stack can be used
to compute the value of a postfix expression such as
shows how a stack can be used
to compute the value of a postfix expression such as
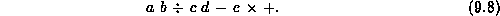
Suppose instead of evaluating the expression we are interested
in constructing the corresponding expression tree.
Once we have an expression tree,
we can use the methods described in Section  to print out the expression in prefix or infix notation.
Thus, we have a means for translating expressions from
one notation to another.
to print out the expression in prefix or infix notation.
Thus, we have a means for translating expressions from
one notation to another.
It turns out that an expression tree can be constructed from
the postfix expression relatively easily.
The algorithm to do this is a modified version of the algorithm
for evaluating the expression.
The symbols in the postfix expression are processed
from left to right as follows:
-
If the next symbol in the expression is an operand,
a tree comprised of a single node labeled with that operand
is pushed onto the stack.
-
If the next symbol in the expression is a binary operator,
the top two trees in the stack correspond to its operands.
Two trees are popped from the stack and
a new tree is created which has the operator as its root
and the two trees corresponding to the operands as its subtrees.
Then the new tree is pushed onto the stack.
After all the symbols of the expression have been processed in this fashion,
the stack will contain a single tree
which is the desired expression tree.
Figure  illustrates the use of a stack
to construct the expression tree from the postfix expression
given in Equation
illustrates the use of a stack
to construct the expression tree from the postfix expression
given in Equation  .
.
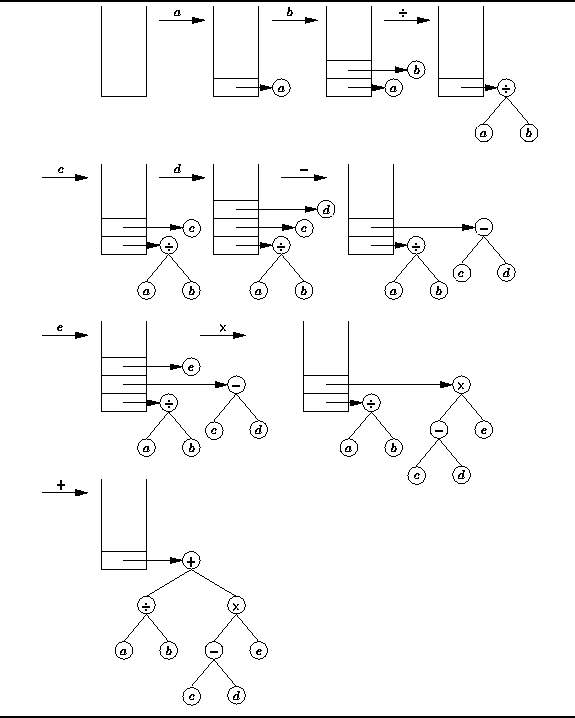
Figure: Postfix to infix conversion using a stack of trees.




 Copyright © 1998 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1998 by Bruno R. Preiss, P.Eng. All rights reserved.
![]() shows how a stack can be used
to compute the value of a postfix expression such as
shows how a stack can be used
to compute the value of a postfix expression such as
![]() to print out the expression in prefix or infix notation.
Thus, we have a means for translating expressions from
one notation to another.
to print out the expression in prefix or infix notation.
Thus, we have a means for translating expressions from
one notation to another.
