The Java Virtual Machine does not support the boolean type directly. As a result, the Java compiler converts every boolean variables to an int. Thus, a Java boolean occupies four bytes. However, since there are only the two values true and false, a single bit is sufficient to hold a boolean value. Therefore, we can realize a significant reduction in the memory space required to represent a set if we use an array of bits. Furthermore, by using bitwise operations to implement the basic set operations such as union and intersection, we can achieve a commensurate reduction in execution time. Unfortunately, these improvements are not free--the operations insert, isMember, and withdraw, all slow down by a constant factor.
Since Java does not directly support arrays of bits,
we will simulate an array of bits using an array of ints.
Program ![]() illustrates how this can be done.
The constant intBits is defined as the number
of bits in a single int.
illustrates how this can be done.
The constant intBits is defined as the number
of bits in a single int.
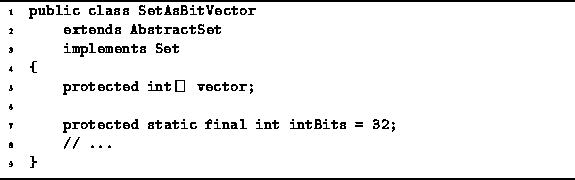
Program: SetAsBitVector fields.