In keeping with the design framework used throughout this text,
we view graphs as specialized containers.
Formally, the graph ![]() is an ordered pair
comprised of two sets--a set of vertices and a set of edges.
Informally, we can view a graph as a container with two compartments,
one which holds vertices and one which holds edges.
There are four kinds of objects--vertices, edges, undirected graphs, and directed graphs.
Accordingly, we define four interfaces:
Vertex, Edge, Graph, and Digraph.
(See Figure
is an ordered pair
comprised of two sets--a set of vertices and a set of edges.
Informally, we can view a graph as a container with two compartments,
one which holds vertices and one which holds edges.
There are four kinds of objects--vertices, edges, undirected graphs, and directed graphs.
Accordingly, we define four interfaces:
Vertex, Edge, Graph, and Digraph.
(See Figure ![]() ).
).
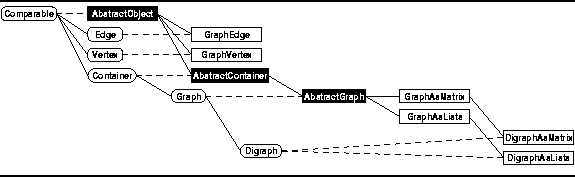
Figure: Object class hierarchy