
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
 |
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
Even simple graphical interfaces often require more than one layout manager. That is, portions of the visible applet region need be laid out differently from other portions. Further, you may want to create compound components, such as a LabeledTextField, that contains both a Label and a TextField. In this section, we describe how multiple components can be combined into a single Container and treated like an ordinary Component for layout and encapsulation purposes. How would you build a telephone key pad object? You could easily set the applet layout manager to GridLayout and then add the keys, however, your whole applet would be a keypad. If you needed the key pad as only a portion of the applet, this simple approach would not work. The solution is to place all the keys in their own Container--that way you can treat the whole key pad like a single Component. Class Panel is normally used to produce compound Component objects as illustrated in the following KeyPad class:
An applet can then instantiate and display KeyPad objects easily:
Corresponding source code:
The containment hierarchy diagram for NestedTest reflects the fact that the main applet contains only two elements--KeyPad containers, which in turn each contain 12 keys: 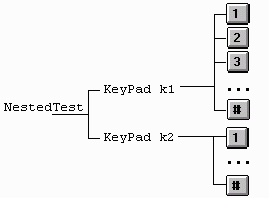
What do you do if you want the key pad to be bigger? The applet's default FlowLayout manager uses the preferred size of each Component when laying them out. The preferred size of the KeyPad will be the combined preferred size of the keys because the KeyPad size is not specified and FlowLayout does not try to stretch its components. To make a bigger key pad, we must set the preferred size of the Keypad Container, which the applet FlowLayout will use to set the size of the KeyPad. We define preferredSize in class KeyPad to return 100x100 so that the applet will stretch the keypad to 100x100 pixels:
The applet then looks like:
It is normally not a good idea to specify the size of components, because different systems have different font and widget sizes, but this example demonstrates how nested containers are used. Related exercises: This section has the following subsection: |
|