In this example we consider the problem of computing a
geometric series summation
for the last time.
We have already seen two algorithms to compute this summation
in Sections ![]() and
and ![]() (Programs
(Programs ![]() and
and ![]() ).
).
An algorithm to compute a geometric series summation
using the closed-form expression (Equation ![]() )
is given in Program
)
is given in Program ![]() .
This algorithm makes use of Program
.
This algorithm makes use of Program ![]() to compute
to compute ![]() .
.
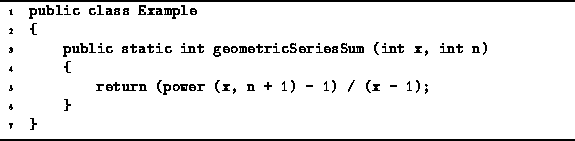
Program: Program to compute ![]() using the closed-form expression.
using the closed-form expression.
To determine the average running time of Program ![]() we will make use of Equation
we will make use of Equation ![]() ,
which gives the average running time for the power method
which is called on line 5.
In this case, the arguments are x and n+1,
so the running time of the call to power is
,
which gives the average running time for the power method
which is called on line 5.
In this case, the arguments are x and n+1,
so the running time of the call to power is
![]() .
Adding to this the additional work done on line 5 gives
the average running time for Program
.
Adding to this the additional work done on line 5 gives
the average running time for Program ![]() :
:
![]()
The running times of the three programs
which compute the geometric series summation
presented in this chapter are tabulated below
in Table ![]() and are plotted for
and are plotted for ![]() in Figure
in Figure ![]() .
The plot shows that,
according to our simplified model of the computer,
Program
.
The plot shows that,
according to our simplified model of the computer,
Program ![]() has the best running time for n<4.
However as n increases,
Program
has the best running time for n<4.
However as n increases,
Program ![]() is clearly the fastest of the three
and Program
is clearly the fastest of the three
and Program ![]() is the slowest for all values of n.
is the slowest for all values of n.
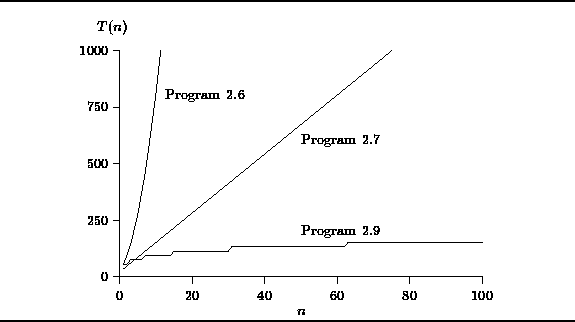
Figure: Plot of running time vs. n for Programs ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.